When RR < 1, OR < 1;Essentially, the odds ratio estimate the _______ in these types of studies Risk ratio What is the definition of odds ratio?An odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make
Hazard Ratio
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk-Relative risk (RR) is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposure Relative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus a nonKeywords hazard ratio, risk ratio, odds ratio Introduction And Background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used forThe Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative RiskRR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to pat
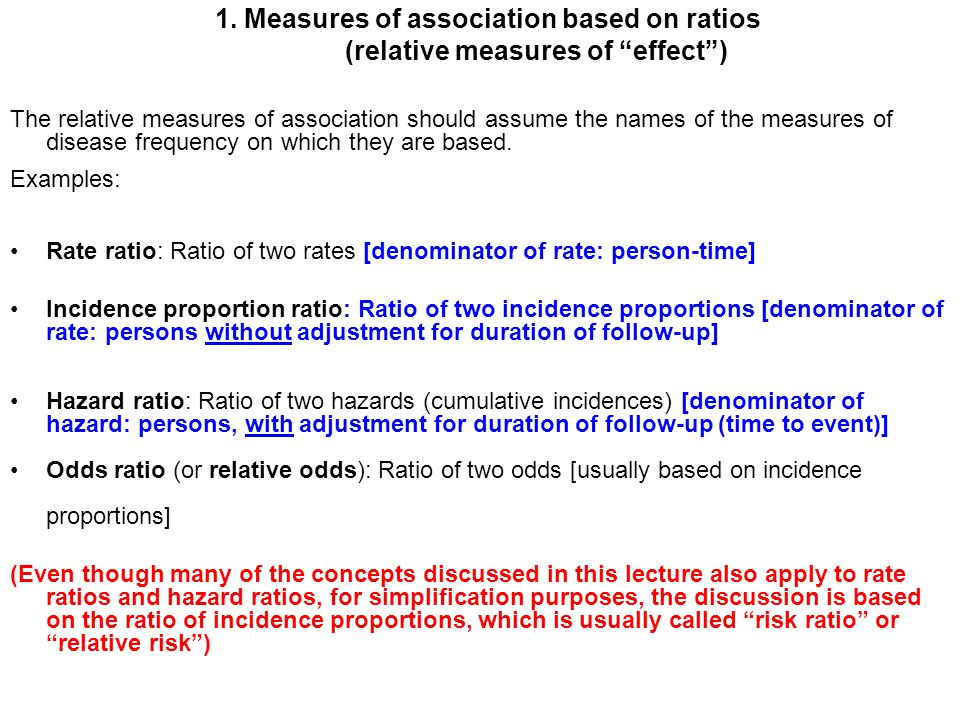
Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidenceOdds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Bila dua kelompok sedang dalam studi atau observasi, Anda dapat menggunakan dua ukuran untuk menggambarkan kemungkinan komparatif sebuah peristiwa yang terjadiKedua ukuran ini adalah odds ratio dan relative risk Keduanya merupakan dua konsep statistik yang berbeda, meski begitu banyak saling berkaitan satu sama lainAs you know a Cox Proportional Regression model (hazard ratio) is the most educated wild ass guess we have!!
Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) RR OR HR Goal Determine relationship in risk status based on some variable Determine association between two variables Determine how one group changes relative to another Use Tells us how an intervention changes risks Tells us if there is an association between an intervention and risk; The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;Relative risk and odds ratio • Odds ratios are used in several statistical analyses because they have useful mathematical properties that make some analyses easier to do • When the disease is uncommon (say
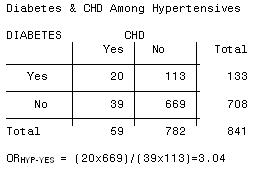



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposure Relative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group Is hazard ratio and odds ratio? The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group The table below shows how the risk ratio wasIf the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities They will always agree on the direction of comparison In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have less heart disease than nonconsumers;




Update In Heart Rhythm Abnormalities And Indications For Pacemaker After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation




Relative And Atribute Risk
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no When events in the intervention group are significantly less frequent than in the control group, then relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will be greater than 10 Introduction In randomised trials and systematic reviews of trials, the effects of new treatments on dichotomousOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR);




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
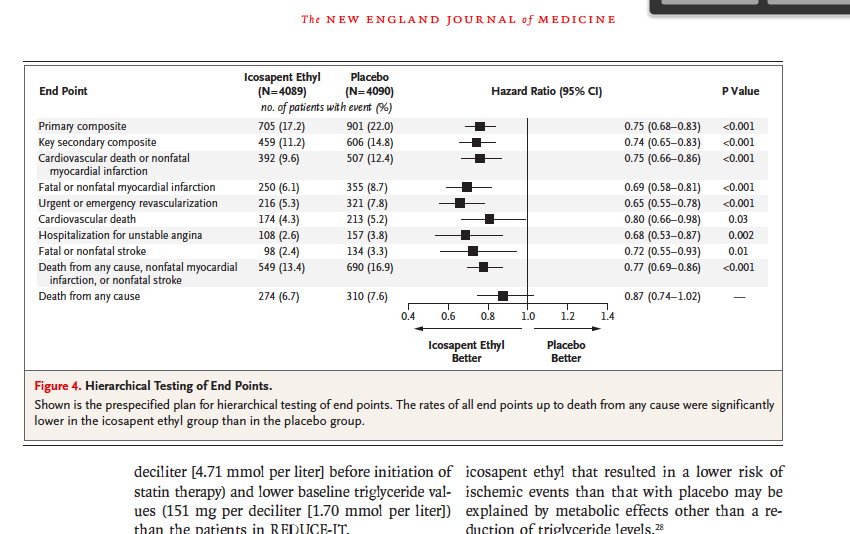



Solved State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com
Odds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio Close 8 Posted by 8 years ago Archived Odds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio I have a background in physics with a few courses in statistics, but I still have a hard time intuitively understanding OR I get RR as it just is a ratio of probabilities, and I look at HR as RR with a time component Every time I see an OR, though, I have to look upHazard ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Despite often being mistaken for being the same thing, relative risk and hazard ratios are nothing alike 3,4 To give an extreme example, the relative risk at time t end when all patients in a cancer trial have died through one cause or another will be 1, while the hazard ratio may be any number from 0 to plus infinity, depending on the actualOdds are the ratio of the probability of an ev ent occurring in a group, divided by the probability of that ev ent not occurring odds = π 1 − π For example, if probability of death in a




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Increase In Hospital Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the numberThe meaning of the odds ratio estimates obtained in a casecontrol study differs according to whether controls are selected from persontime at risk (the study base), persons at risk (the basepopulation at risk at the beginning of followup), or survivors (the population at risk at the end of followup) It would then be nice, if odds ratio was close to relative risk While the impact ofSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a studyOdds that a person with an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed)/ Odds that a person without an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed) Odds group 1/odds group 2This is called the odds ratio;




Statistics You Can Use Practical Use Of Statistics



Hazard Ratio
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Relative risk vs Odds Ratio vs Hazard Ratio Relative risk and risk ratios (probabilitiy ratios) are different from odds ratios, although they might be close in certain cases Even though odds ratios have more practical applications, relative risk is arguably a more intuitive measure of effectiveness and so has its applications in fields like epidemology, clinical research including randomized The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab)) Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of these metrics Yet odds ratio is strongly preferred as the "right" metric to report in almost all scenarios That




Relative Risk Wikipedia




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times The term is typically used in the context of survivalFor multiple logistic regression, and Cox proportional model, each publication may adjust difference factors or confounders, say in the renal failure study, the proteinuria might be the risk factor cause the renal failure This factor maybe included in theRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized Keywords hazard ratio




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR One of the main differences between risk ratio and hazard ratio is that risk ratio does not care about the timingUnderstanding Relative Risk, Odds Ratio, and Related Terms As Simple as It Can Get Chittaranjan Andrade, MD ABSTRACT Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know how these statistics are derived and interpreted, nor are all readers aware of theirRelative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will be greater than 10 Key words clinical trials, number needed to treat, odds, statistics (Aust Prescr 08;3112–16) Introduction In randomised trials and systematic reviews of trials, the effects of new treatments on dichotomous outcomes (such as




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet
Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases ofThis is why the first study yielded odds ratios and not relative risk Once they got the results and found smoking to have the strongest association, they reversed the roles and did a cohort study looking at smokers and nonsmokers (now the independent variable) and compared their lung cancer status (now the dependent variable), yielding relative risk ratios The difference is theOdds Ratio Vs Risiko Relatif Ketika dua kelompok sedang dipelajari atau diamati, Anda dapat menggunakan dua ukuran untuk menggambarkan kemungkinan komparatif dari suatu peristiwa terjadi Dua ukuran ini adalah rasio odds dan risiko relatif Keduanya adalah dua konsep statistik yang berbeda, walaupun begitu banyak saling terkait satu sama lain




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
N = 905 6;N = 787 7; How do you interpret odds ratio and relative risk?




Applied Statistics Relative Risks Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Nnt Nnh Flashcards Quizlet




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
5 studies) in veterans, and 211 (95% CI , I2= 912%, P < 0001;Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR =Odds ratio and relative risk




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And
All figure content in this area was uploaded by Janez Stare, Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific When the outcome risk is 01 or less, odds ratios and risk ratios agree well for risk ratio values ranging from 01 to 10 in all 3 figuresOdds Ratio (OR) vs A hazard ratio is Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
Also odds ratio with odds ratio, relative risk with relative risk, hazard ratio with hazard ratio, can we combine them together?RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR will




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




How Did Researchers Calculate The Hazard Ratio Cross Validated
When RR = 1, OR = 1 ;This implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionThe hazard ratio




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference The Journal Of Family Practice Data Science Study Plan Clinical Trials
Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risks that happen before theRelative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, and in cohort studies in which the outcome occurs in less than 10% of the unexposed population, the OR provides a reasonable approximation of the RR However, when an outcome is common (iY 10% in the unexposed group), the OR will exaggerate the RR One If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds of an event in the control group The term 'Odds' is commonplace, but not




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



1
3 studies) in the general population Relative risk and risk ratios (probabilitiy ratios) are different from odds ratios, son of risks between groups, the ratio of risks, or the relative risk, is a statistic of choice Pooled HR was 161 (95% CI ;When RR > 1, OR > 1;




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
I2= 809%, P < 0001; Note that the odds ratio and relative risk are both greater than 1, which tells us that the chances of experiencing some event (eg passing the skills test) is greater in the treatment group compared to the control group The odds ratio and relative risk give us similar information, but we interpret each value in slightly different ways In particular The odds ratio tells us that the odds




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities Dagger 1 Dagger 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document
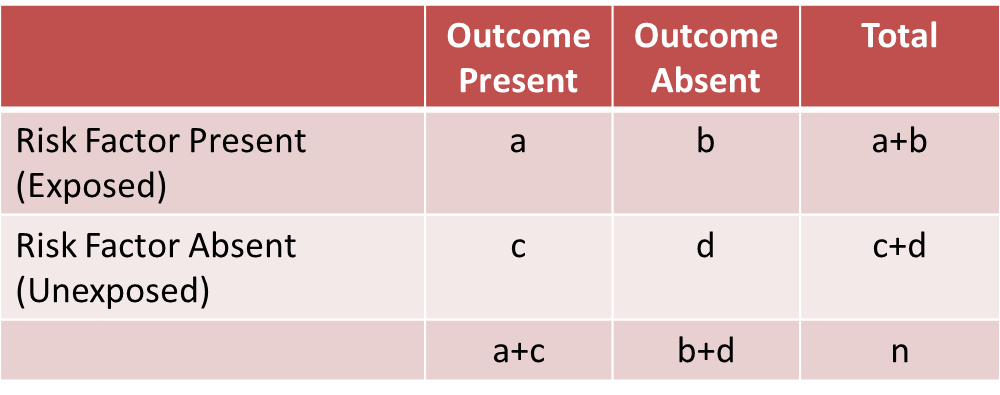



A Stratified Analysis




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
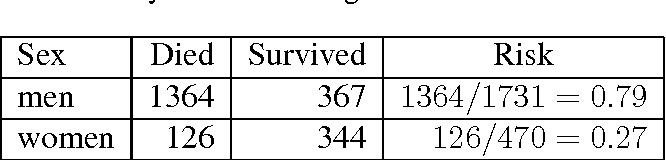



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




상대위험도 Relative Risk Vs 오즈비 Odds Ratio




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



Wrnmmc Libguides Com




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Odds Ratio Article




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Lincom Stata




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Risk Factors Explained V01




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Hazard Ratio Measure Of Survival Or Time To Event Analysis Same As Relative Risk 1 Means The Hazard Ratio Analysis University Of Alabama At Birmingham




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Learning And Applying Biostatistics How The Guinness Brewery




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



Attributable




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases
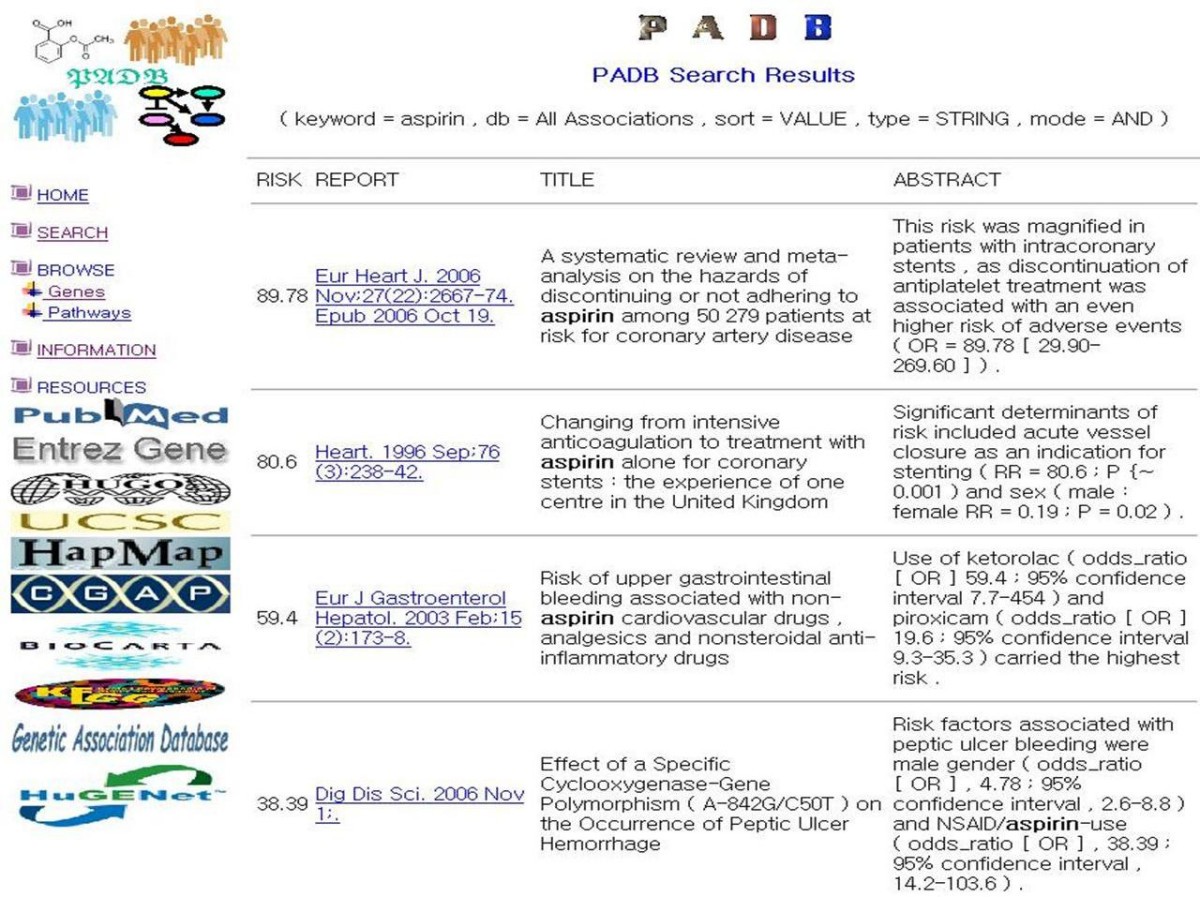



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



Odds Ratio



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube
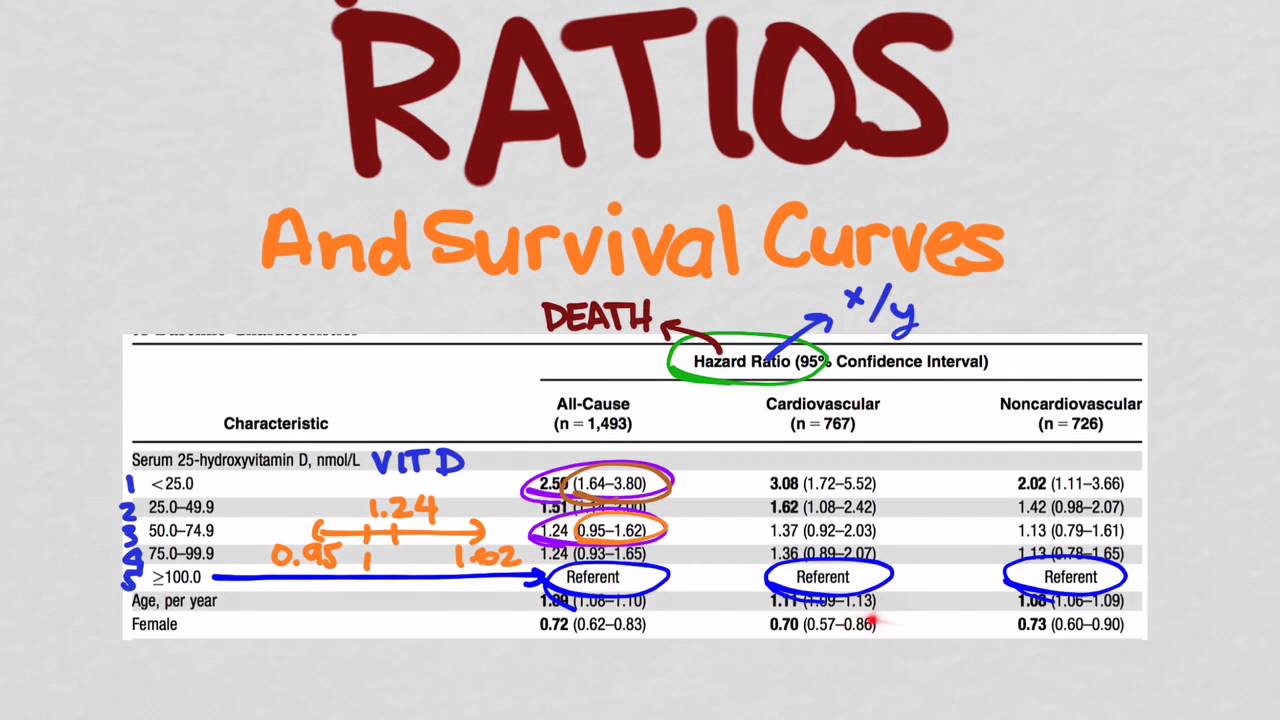



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Epidemiologic And Research Applications In Community Nursing Lecture




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿